NMPA officially approved aCGT's "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" to enter clinical trials
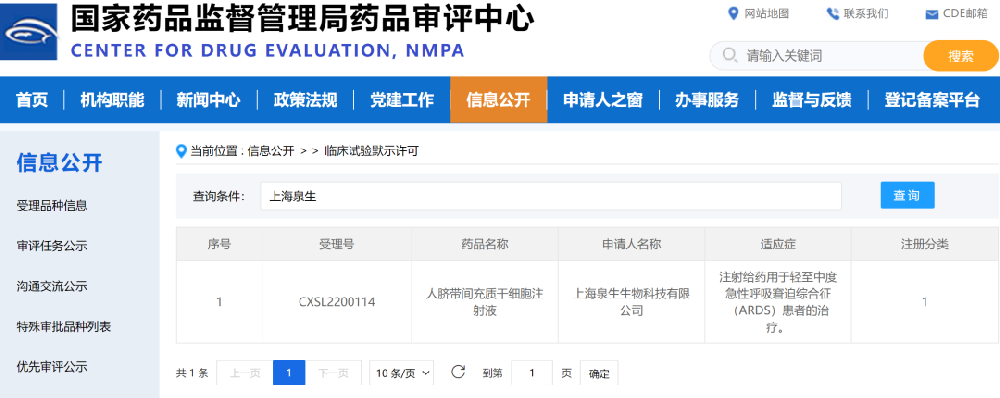
On May 26, 2022, the Class I biological product independently developed by Asia Cell Therapeutics (Zhejiang) Co., Ltd. (aCGT), "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" (NO. CXSL2200114), has officially obtained the drug clinical trial approval from the Center for Drug Evaluation of the National Medical Products Administration (CDE). The official website of the National Medical Products Administration: aCGT "human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection" has been implicitly approved for clinical trials Notice of approval of drug clinical trials by NMPA The approval of IND marks a milestone in the development of new stem cell drugs by aCGT, and it is also expected to become the world's first new stem cell drug for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), with significant value for the entire stem cell therapy field. 1. What is acute respiratory distress syndrome? 1. Causes of ARDS Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) refers to the excessive activation of an inflammatory response in the lungs or even throughout the body due to various causative factors. It is characterized by destruction of the pulmonary epithelium and vascular endothelium, decreased alveolar clearance, and diffuse alveolar injury on imaging. Alveolar epithelial injury and pulmonary endothelial injury caused the accumulation of protein-rich inflammatory edema fluid in the alveolar cavity in the pathological samples of the patient. To put it simply, it is the leakage of fluid from the blood vessels into the alveoli, making it difficult for the patient to breathe, or even unable to breathe. There are many factors that cause ARDS, such as sepsis, multiple injuries, massive blood transfusions, aspiration pneumonia, pulmonary contusion and cardiopulmonary bypass, among which sepsis and severe lung infection are the main causes of ARDS in clinical practice. Studies have shown that among the first 41 patients admitted to the hospital in Wuhan, ARDS was the fatal complication with the highest incidence (29%). 2. Pathogenesis of ARDS The pathogenesis of ARDS is complex, and the currently recognized mechanism is that various etiologies induce an increase in the production of pro-inflammatory factors in the lungs, and the release and activation of a large number of inflammatory factors make the inflammatory response in the lungs uncontrollable, and the pulmonary capillary endothelial cells and alveolar epithelial cells are damaged, resulting in dysfunction. The release of reactive oxygen species from injured endothelial cells can increase the permeability of lung endothelial cells, and a large amount of protein-rich substances enter the bronchial and alveolar spaces, resulting in pulmonary edema, thereby reducing the efficiency of pulmonary ventilation and even respiratory failure in the body, which is difficult to correct. 3. Traditional treatment modalities for ARDS Currently, treatment for ARDS includes primary disease treatment, protective mechanical ventilation, and pharmacotherapy. However, neither anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., corticosteroids) nor drugs that attempt to improve the lungs themselves (e.g., inhaled β agonists) can effectively reduce the mortality rate of ARDS, and mechanical ventilation is still the main clinical treatment. However, mechanical ventilation uses a ventilator to control the air pressure to expand the alveoli, which may cause alveolar wall damage and further induce mechanical ventilation-related lung injury. 4. The importance of developing effective drugs for the treatment of ARDS ARDS is a common critical illness in clinical practice, one of the main causes of respiratory failure, and has a high mortality rate in ICU patients. Epidemiological studies show that there are about 3 million ARDS patients in the world every year, and the incidence rate of intensive care unit patients is about 10%, and the mortality rate is 30%~40%. So far, there is still a lack of breakthroughs in the international medical community for the treatment of ARDS, and many drugs that have shown potential in preclinical studies have failed to succeed in clinical trials, and the novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic has further highlighted the importance of developing effective drugs for the treatment of ARDS. 2. Stem cell therapy for acute respiratory distress syndrome With the advancement of basic research in recent years, the relevant mechanisms of ARDS have been continuously revealed. Due to the complexity of the cause and pathology of this disease, it may be a valuable research direction to carry out targeted multi-means combination therapy according to the actual situation of patients. As a new type of treatment, stem cell therapy has attracted widespread attention, and stem cell therapy has obvious effects in many diseases. For example, liver failure, osteoarthritis, GVHD, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases have become popular research directions in the medical field. Numerous studies have confirmed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also have a good therapeutic effect in lung injury: 01 MSCs have differentiation and regenerative repair functions Exogenous MSCs can "homing" at the site of injury to induce differentiation into lung tissue cells such as mesenchymal fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, lung epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells, thereby alleviating lung injury. 02 MSCs have immunomodulatory functions MSCs have an inhibitory effect on the inflammatory response to ARDS overactivation. In addition, MSCs can also inhibit inflammatory levels by secreting a series of anti-inflammatory cytokines, while regulating the function of body systems, enhancing bacterial clearance, reducing bacteremia, and improving pulmonary vascular permeability. 03 MSCs have paracrine effects MSCs secrete a variety of cytokines and active metabolites into the microenvironment to reduce inflammation. For example, IL-6, PGE-2, and IL-10 secreted by MSCs inhibit T cell proliferation and prevent dendritic cell maturation. Other cytokines and a range of proteoglycan complexes have also been shown to inhibit the inflammatory response of overactivity in damaged areas. MSCs release particulates into the environment. A microparticle is a biologically active small membranous vesicle containing proteins, mRNA, miRNA, and other bioactive substances that can be used as mediators to participate in cell-to-cell "communication" and regulate immune cell behavior. aCGT’s "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" can inhibit the inflammatory response of ARDS overactivation, which can safely and effectively solve the "root cause" of the disease, and treat and overcome ARDS from the essence of the disease. In addition, based on the regeneration, repair, immune regulation and paracrine characteristics of stem cells,aCGT's "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" can be used for the treatment of a variety of other major and difficult diseases, including non-specific inflammatory therapy, tissue regeneration, autoimmune diseases and other directions. The aCGT scientific research team has always adhered to the center of patient benefits, promoted the clinical research of stem cell products with high quality, transformed more technical reserves into clinically reliable products, and practiced the sacred mission of giving everyone the opportunity to have the right to speak about life.